Renewable power sources are reshaping how we think about and utilize resources to power our lives. This guide explores the major renewable energy sources, offering a deep understanding of their workings, benefits, and practical applications.
The focus here is not just on the theoretical aspects, but also on how these sources can be realistically implemented in various settings.
Harnessing the Sun’s Abundance
Solar power, derived from the sun’s rays, is a cornerstone of renewable resources. Solar panels, or photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight directly into electricity. These panels can be installed on rooftops, in large outdoor solar farms, or even in small portable devices.
The technology is constantly evolving, becoming more efficient and less expensive, making it a viable option for individual households and large-scale power generation.
Solar power is clean, abundant, and increasingly cost-effective, though its efficiency can be weather-dependent and requires significant initial investment. Check this to learn more about renewable sources of energy.
Wind Energy
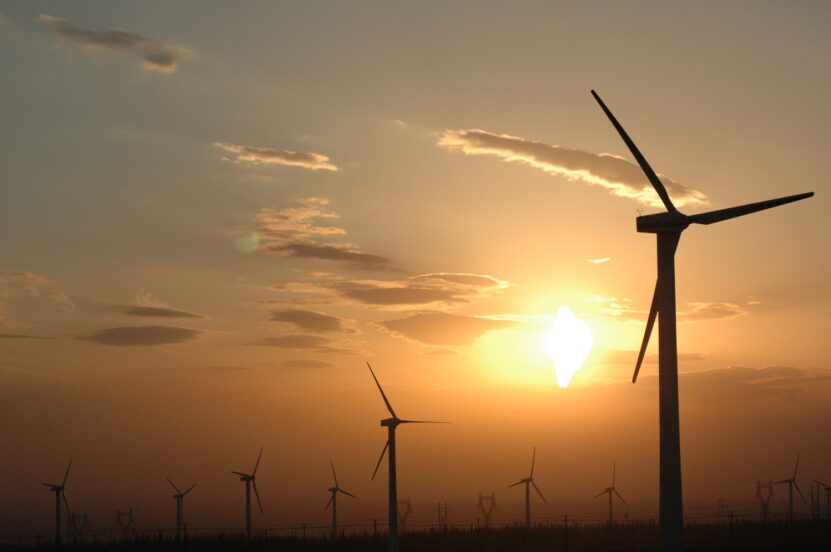

Wind energy, generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into electricity using turbines, is a rapidly growing sector. Wind farms, consisting of numerous large turbines, can be located on land or offshore. The effectiveness of wind turbines depends on location, with certain areas having more consistent and stronger winds.
While wind energy is clean and efficient, the turbines require significant space and can impact local wildlife and aesthetics.
Flowing Water as a Powerful Ally
Hydropower is one of the oldest and most established forms of renewable power. It utilizes the energy of flowing water, typically from rivers or dams, to generate electricity. Hydropower plants can range from massive installations like the Hoover Dam to small, community-run projects.
This source is highly efficient and reliable but can have significant ecological impacts, such as altering water ecosystems and affecting fish populations.
Earth’s Inner Heat as a Resource
Geothermal energy exploits the heat from the Earth’s core to generate power. This can be harnessed by tapping into underground reservoirs of steam or hot water, which can then be used to drive turbines.
Geothermal plants are generally located in regions with volcanic activity, where Earth’s heat is closer to the surface. This power source is incredibly consistent and has a small land footprint, but exploration and drilling can be expensive and technically challenging.
Organic Materials as Fuel
Biomass energy involves using organic materials – such as plant matter and animal waste – to produce electricity, heat, or even transportation fuels. This can be achieved through direct combustion, or by converting these materials into biofuels.
Biomass is a versatile energy source and can be a way to manage waste, but it requires careful management to ensure that its use is truly sustainable and does not lead to deforestation or other environmental issues.
Exploring Marine Power Potential
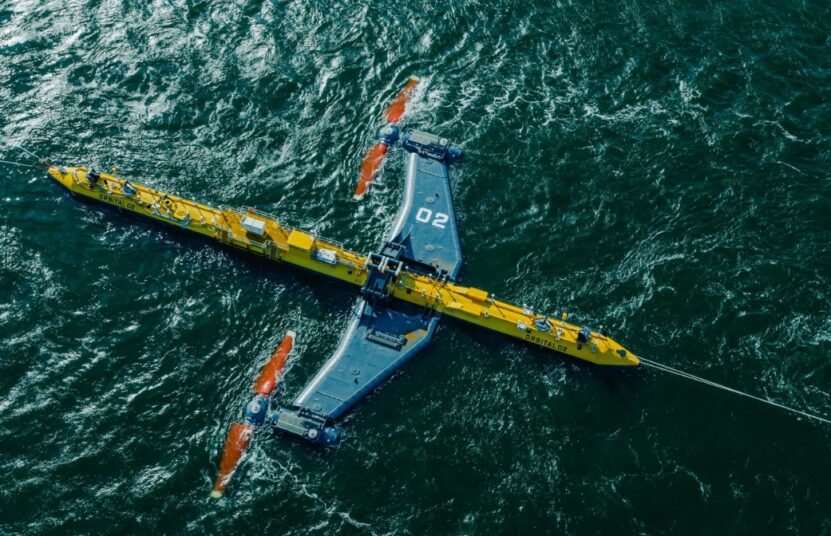

Ocean energy encompasses a range of technologies that generate power from the sea, including tidal, wave, and ocean thermal energy conversion. These methods exploit the natural movements and temperature differences in the oceans.
While promising, ocean energy technologies are still largely in the developmental stage, facing challenges in terms of cost, environmental impact, and technical feasibility.
Implementation and Practical Considerations
Adopting these renewable power sources isn’t just about installing the technology; it involves considering the local environment, energy needs, and economic factors. For instance, solar panels are more suitable in areas with high sun exposure, while wind turbines require open, windy landscapes.
Moreover, transitioning to renewable resources often requires significant upfront investment, but this can be offset by long-term savings and government incentives.
Integrating Renewables into the Grid
The integration of renewable sources into the existing power grid is a critical aspect of the renewable energy transition. This requires not just physical infrastructure, but also advanced grid management technologies.
Smart grids, which use information and communication technologies to manage electricity flow, are key to efficiently incorporating variable energy sources like solar and wind.
Storage solutions, such as batteries, are also crucial to balance supply and demand, storing excess power generated during peak production times for use during periods of low generation.
Economic and Policy Drivers
The economics of renewable power are rapidly becoming more favorable, driven by technological advancements and scale economies. However, policy frameworks play a crucial role in this transition.
Government incentives, such as tax credits, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs, have been instrumental in promoting renewable energy adoption.
Additionally, setting targets for renewable energy production and implementing carbon pricing can create a more level playing field between renewable and fossil fuel-based power.
Community and Decentralized Systems

Renewable energy offers unique opportunities for community and decentralized power systems. Unlike traditional large-scale power plants, renewable installations can be scaled down to suit local needs, providing communities with greater energy independence and resilience.
Decentralized systems, particularly in rural or remote areas, can reduce the need for extensive grid infrastructure and lower energy costs.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability
While renewable power sources are far more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels, they are not without their impacts. The manufacturing of solar panels and wind turbines, for instance, does require resources and energy.
However, the overall lifecycle emissions and environmental footprints are significantly lower. Sustainable management, such as responsibly sourcing materials and recycling old equipment, is essential to minimize these impacts.
The Role of Innovation and Research
Ongoing research and innovation are pivotal in advancing renewable energy technologies and reducing costs. Emerging technologies, like floating solar panels and advanced wind turbine designs, promise to open up new possibilities.
Additionally, improvements in energy efficiency and battery technology can enhance the effectiveness and feasibility of renewable installations.
Future Trends
The future of renewable energy is not just about individual technologies, but how they can work together to create a holistic and sustainable energy system. Innovations in grid management, storage, and energy efficiency, combined with favorable economic and policy environments, will be key to realizing this future.
As societies globally acknowledge the urgency of addressing climate change, renewable energy stands as a beacon of hope and a practical pathway to a cleaner, more sustainable world.
End Note
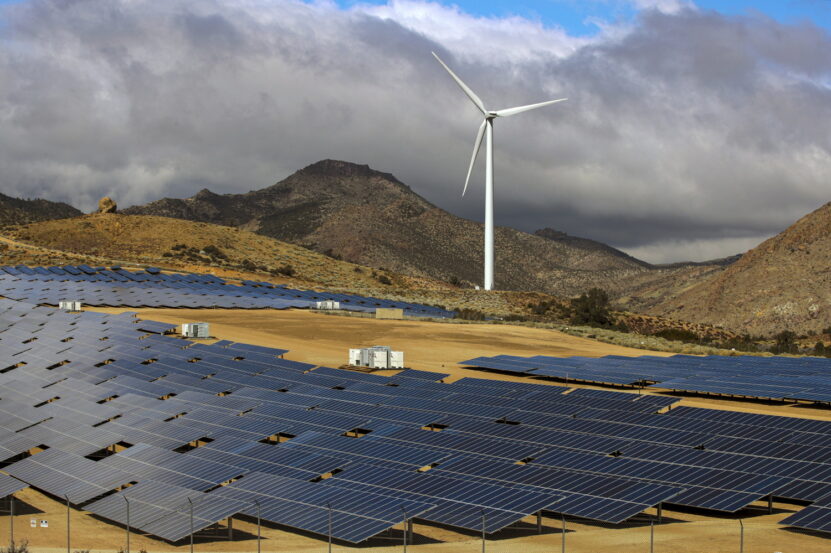

In summary, the journey towards renewable energy is multifaceted, involving technological, economic, and social dimensions. It’s a path that requires careful consideration of local conditions and needs, but offers enormous benefits in terms of sustainability, independence, and economic growth.
The shift to renewables is not just an environmental imperative but an opportunity to reimagine how we power our world.
Related Posts:
- Visa Choices for UK Weddings: A Practical Guide with…
- Pet-Proofing Your Space: A Practical Guide to When…
- How Is Olive Oil Made: A Comprehensive Guide with…
- How To Fix Xbox HDMI Not Working - A Comprehensive…
- How to Reset Xbox Controllers for Xbox One, Xbox…
- Is 9Cr18MoV Steel Good for Knives? A Comprehensive…