Cardiovascular endurance stands as a cornerstone for a healthy, active life. It’s the stamina that powers your heart, lungs, and muscles, enabling you to thrive during prolonged physical activities. Beyond regular exercise, nutrition plays a pivotal role in enhancing this endurance.
This blog unveils 10 nutrition tricks, each backed by science, poised to significantly boost your cardiovascular endurance. These insights aim to serve as your dietary compass, guiding you towards choices that enrich not just your workouts, but your overall well-being.
1. Stay Hydrated
Hydration is the silent champion of endurance. It’s not just about quenching thirst; staying hydrated is about ensuring the optimal performance of every cell in your body. For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, proper hydration maintains blood volume, regulates body temperature, and facilitates muscle function.
The general recommendation is to drink 8-10 glasses of water daily, but this can vary based on individual needs, especially during intense training.
To seamlessly integrate hydration into your daily routine, consider carrying a water bottle at all times, incorporating water-rich foods like cucumbers and watermelons into your diet, and developing a habit of sipping water throughout the day, even before the thirst sets in. Visit this link for more info on this subject.
2. Balanced Diet
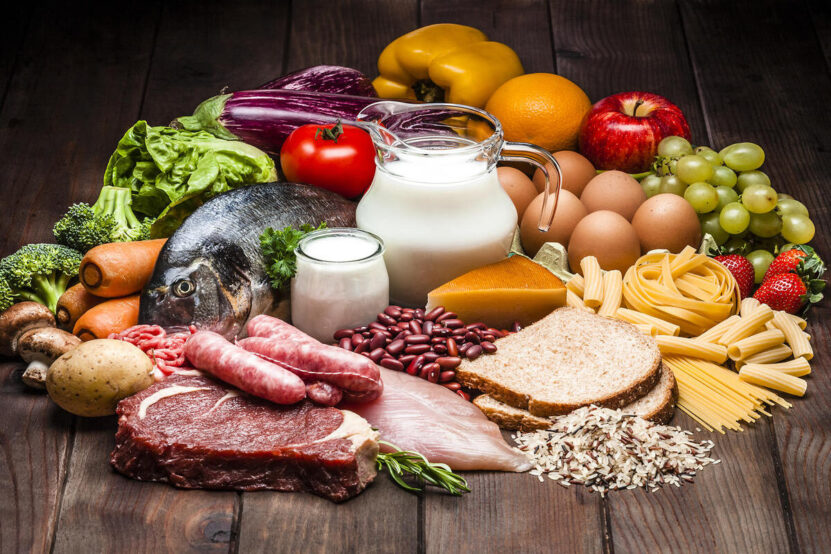

A balanced diet is the bedrock of peak physical performance and cardiovascular endurance. It’s a harmonious blend of carbohydrates for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and fats for overall health.
Carbohydrates, particularly from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, should take center stage in your meals, providing the necessary fuel for your workouts. Proteins, sourced from lean meats, dairy, or plant-based alternatives like beans and lentils, are crucial for muscle repair and recovery.
Fats, often misunderstood, are essential too, especially the unsaturated kind found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish. They provide a long-lasting energy source and are fundamental for absorbing vitamins and protecting your heart health.
3. Carbohydrates for Energy
Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy currency of your body, especially during endurance activities. However, not all carbs are created equal. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables, break down slowly, providing a steady stream of energy and keeping blood sugar levels stable.
On the other hand, simple carbohydrates, found in fruits and sweetened snacks, offer a rapid energy boost but can lead to energy crashes if not balanced with other nutrients.
For sustained energy and optimal performance, focus your diet on complex carbohydrates, pairing them with proteins and fats to ensure a steady, reliable energy flow during your endurance activities.
4. Proteins for Muscle Repair
Proteins are the building blocks of muscle repair and growth. Every bout of physical activity tears muscle fibers, and proteins step in to repair and strengthen these fibers, paving the way for muscle growth and improved endurance.
Sources of high-quality protein include lean meats like chicken and turkey, fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, and plant-based options such as beans, lentils, and tofu. Incorporating these protein sources into your meals not only facilitates muscle repair but also contributes to a feeling of fullness, aiding in overall weight management and health maintenance.
5. Healthy Fats
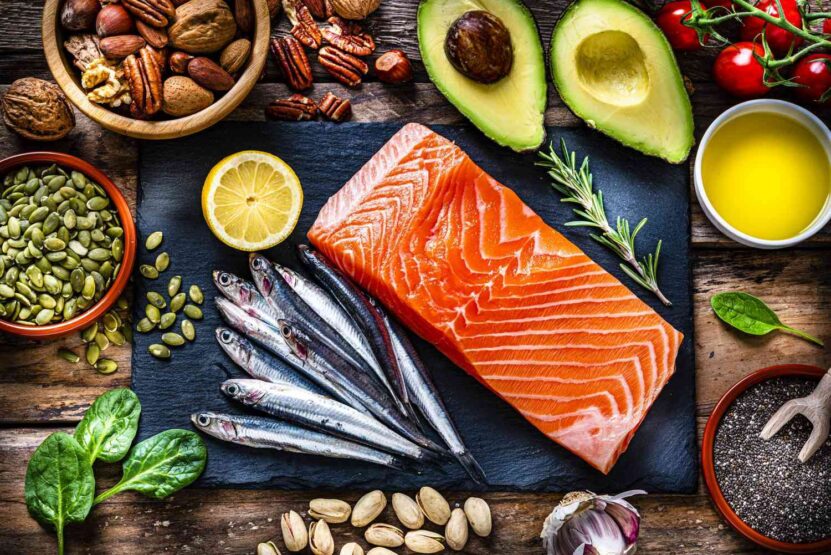

Healthy fats, often overshadowed by their unhealthy counterparts, are vital for endurance athletes. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, provide a dense energy source and play a crucial role in maintaining heart health and reducing inflammation.
These fats also assist in the absorption of essential vitamins and provide the building blocks for hormone production, crucial for overall health and optimal physical performance. Incorporating a moderate amount of these healthy fats into your daily diet ensures you have a balanced energy reserve, supporting your endurance endeavors.
6. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are the unsung heroes of peak physical performance. These essential nutrients, though required in smaller quantities, have a colossal impact on your body’s functioning and your overall endurance.
Key players include iron, which is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood, calcium and vitamin D for strong bones, and electrolytes like sodium and potassium for muscle function and hydration.
A diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, dairy, and whole grains typically covers your spectrum of vitamins and minerals, fortifying your body against fatigue and bolstering your endurance capacity.
7. Antioxidants
Antioxidants are your body’s defense mechanism against oxidative stress, a byproduct of intense physical activity. They neutralize free radicals, protecting your cells from damage and inflammation.
This protection is crucial for endurance athletes, as it aids in reducing muscle soreness and speeding up recovery. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries, dark chocolate, nuts, and green leafy vegetables.
Regularly incorporating these foods into your diet not only provides a shield against oxidative stress but also supports overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases and keeping your body in top form for endurance activities.
8. Pre-Workout Nutrition

The meal or snack you consume before your workout can significantly influence your performance. The ideal pre-workout nutrition strikes a balance between carbohydrates and proteins, providing a sustained energy source and preventing muscle breakdown.
This meal should be relatively light and consumed about 1-2 hours before exercising to allow for digestion. Some effective pre-workout foods include a banana with a spoonful of peanut butter, a small serving of oatmeal with berries, or a whole-grain toast with lean turkey. These options provide the right mix of nutrients to fuel your workout without weighing you down.
9. During-Exercise Fuel
For endurance activities lasting more than an hour, refueling during the exercise becomes crucial. The goal here is to replenish energy stores and maintain hydration to prevent fatigue and performance decline.
Sports drinks can provide a quick supply of easily digestible carbohydrates as well as electrolytes to replace those lost through sweat. Energy gels, while convenient, should be used judiciously and in combination with water to aid absorption.
Alternatively, small snacks like a handful of raisins or a banana can offer a natural, easy-to-digest carbohydrate source. The key is to listen to your body and provide it with the fuel it needs to maintain a consistent performance throughout your endurance activity.
10. Post-Workout Recovery
The period immediately following your workout is critical for recovery and preparing your body for the next session. Post-workout nutrition should focus on replenishing glycogen stores with carbohydrates and repairing muscles with proteins.
A ratio of 3:1 carbohydrates to protein is generally recommended. Good post-workout meal choices include a smoothie made with fruits and a scoop of protein powder, a chicken sandwich on whole-grain bread, or a serving of quinoa with mixed vegetables and lean meat.
Timely consumption of these nutrients aids in muscle recovery, reduces soreness, and ensures you’re ready for your next endurance challenge.
Conclusion
Improving cardiovascular endurance is a multifaceted endeavor, with nutrition playing a pivotal role. The 10 nutrition tricks discussed in this post provide a roadmap to enhance your endurance through informed dietary choices.
From staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet to optimizing your pre-workout and recovery meals, each strategy is a step towards a fitter, more resilient you. Embrace these dietary changes and witness a tangible enhancement in your endurance, energy, and overall fitness.
Remember, the synergy between nutrition and physical activity is undeniable, and mastering this relationship is key to unlocking your full endurance potential.